

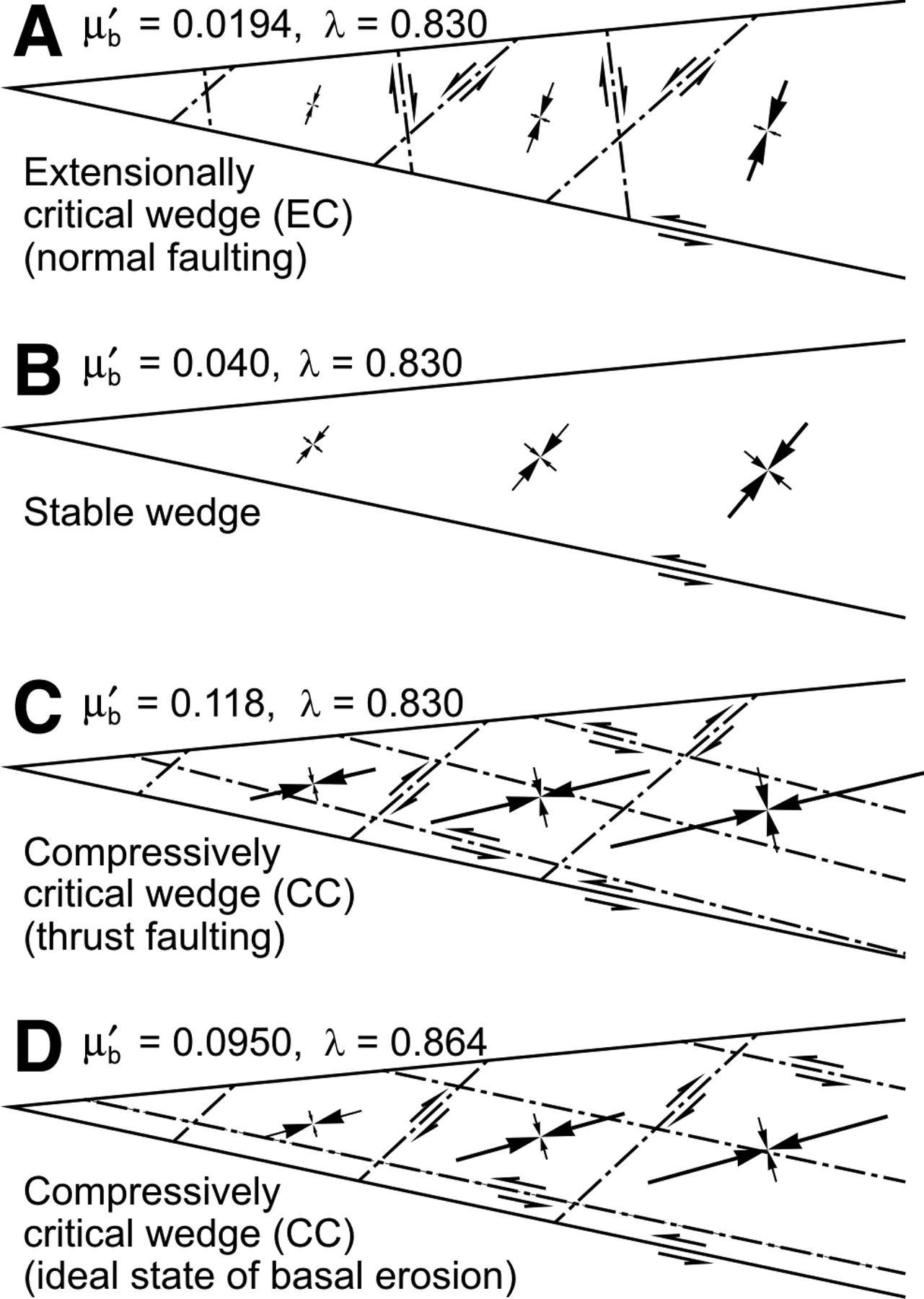
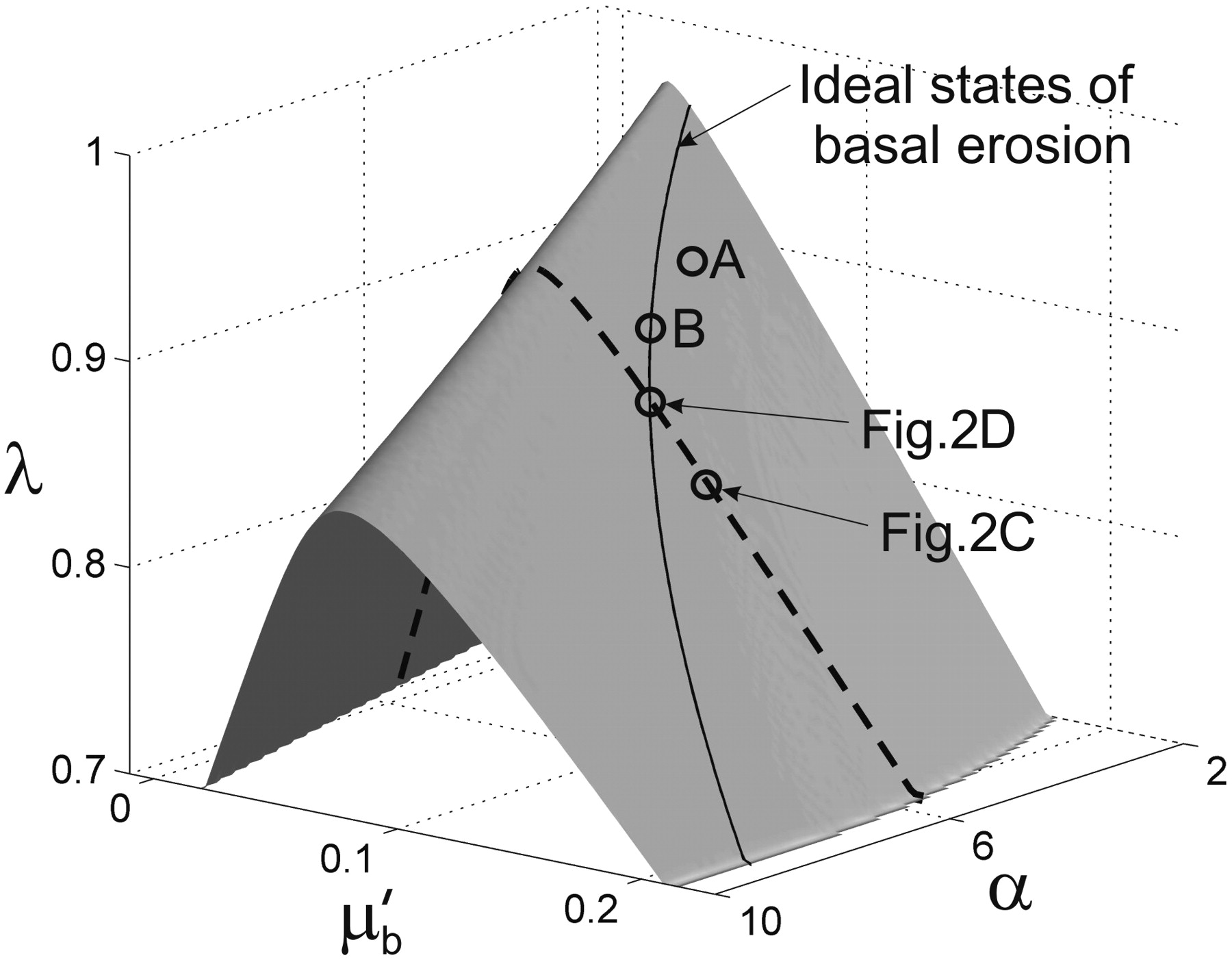
In this model, basal erosion occurs during large earthquakes when the shallow, rate-strengthening part of the plate interface strengthens and its overlying wedge weakens, but extension occurs during interseismic relaxation of wedge stress.
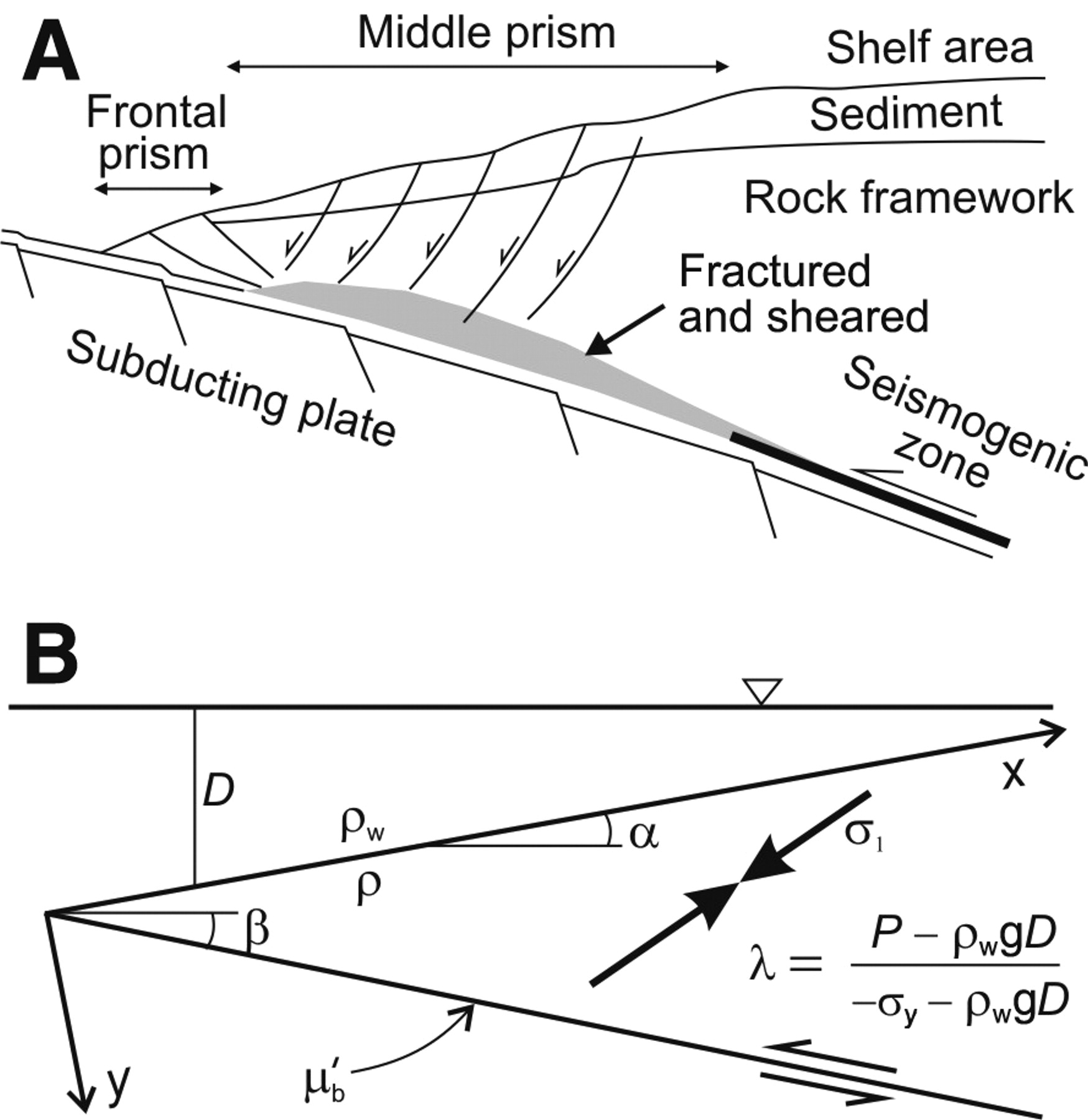
The mechanics of basal erosion provide important information on the nature of the updip limit of the megathrust seismogenic zone in margins dominated by basal erosion.
This work was published on Geology:
Wang, K., Y. Hu, R. von Huene, & N. Kukowski (2010), Interplate earthquakes as a driver of shallow subduction erosion, Geology, 38(5), 431-434, doi: 10.1130/G30597.1. Link
Copyright © Geodynamics Research Center,USTC/DSEL All Rights Reserved